Content

process costing is a system of product cost allocation used in merchandising and industry. The main objective is to allocate total manufacturing costs to the various products according to the proportion of resources consumed by each product. Under process costing, the procedure used to manufacture a product is divided into well-defined processes.
First-in-first-out Inventory MethodUnder the FIFO method of accounting inventory valuation, the goods that are purchased first are the first to be removed from the inventory account. As a result, leftover inventory at books is valued at the most recent price paid for the most recent stock of inventory. As a result, the inventory asset on the balance sheet is recorded at the most recent cost. These costs are accumulated from the first process to the last process. The said is then bifurcated into an inventory of complete products & inventory of products that are under process.
Accounts Used to Track Product Costing
The difficulty experienced in allocating the cost, when work done is expressed both in terms of finished units and unfinished units, can be visualised by comparative study of statements in case A and case B. The effect of using LIFO method, FIFO method and average method will be different on the unit cost of the process. First step is to trace the physical flow of production. For this purpose a statement is prepared showing input and output of the process in physical units. To calculate the profit or loss of each process as the product may be sold after completing any of the process on the raw material. To calculate the cost of production of joint products and by-products separately.
For these companies, it can be difficult or impossible to directly allocate costs to each item as it moves through the manufacturing process. https://www.bookstime.com/ enables companies to estimate item costs by adding up the expenses of each step in the manufacturing process, then dividing by the number of items. To ensure accuracy, companies need to include only product-related costs from each department involved in the process and correctly allocate cost to work-in-progress at each stage. Figure 4.1 shows how product costs flow through accounts for job costing and process costing systems.
Using the Process Costing Method
The company draws up a floor plan and measures how many square feet each department uses. Expenses can be allocated to different processes on rational basis and accurate cost, thus, can be ascertained. Cost Control – Being each process is standardised and stable and can be predetermined so control is easier. Separate Entity – In contract costing every contract is a separate entity. Cost of process can be obtained even if product is incomplete.
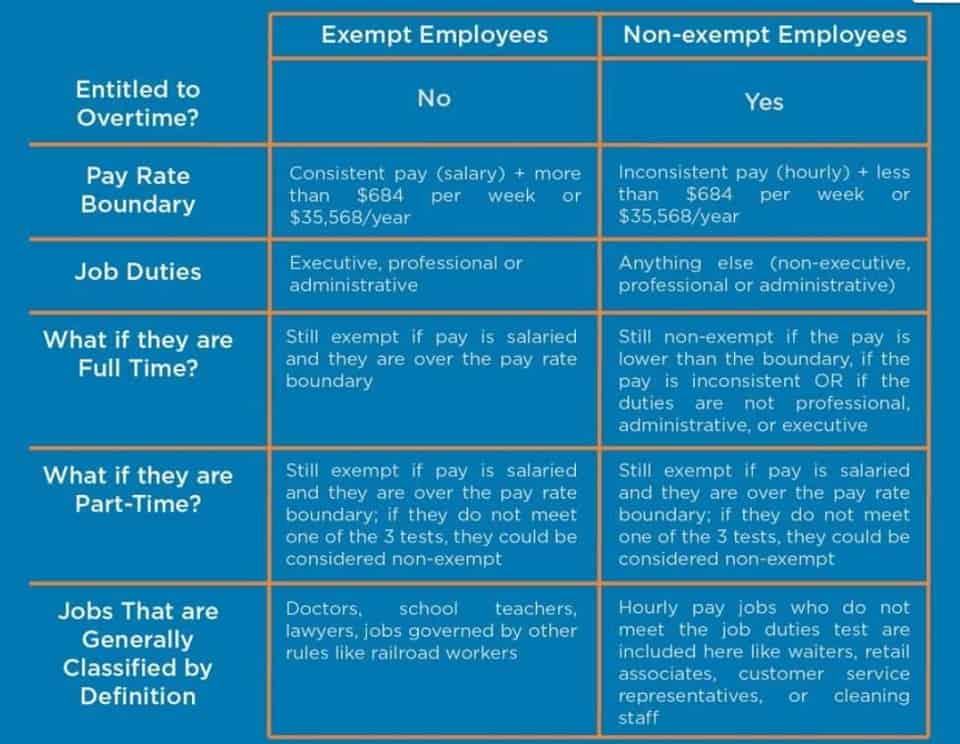
Examine the graphic below that compares job and process costing, noting in particular the difference in how costs are shifted out of work in process. Process costing entails handing off accumulated costs from one department to the next. Process costing is an accounting methodology that traces and accumulates direct costs, and allocates indirect costs of a manufacturing process. Costs are assigned to products, usually in a large batch, which might include an entire month’s production. Eventually, costs have to be allocated to individual units of product. It assigns average costs to each unit, and is the opposite extreme of Job costing which attempts to measure individual costs of production of each unit.
Basic Managerial Accounting Terms Used in Job Order Costing and Process Costing
Therefore, it is important to keep track of the cost per unit in order to make sure that the product is profitable. Fifth, allocate the relevant costs to the units of product completed and to the units of product remaining in the work-in-process account.
- Average method is used when opening WIP is given in terms of materials, labour and overhead but the degree of completion is not mentioned.
- In operation costing, each operation is treated as a cost centre and the costs are accumulated for each operation instead of each process.
- It also enables companies to hone in on the cost of each stage in the manufacturing process and look for ways to reduce cost if necessary.
- In contrast with job costing, which measures costs based on individual jobs, process costing measures costs based on each unit of output produced.
For example, when an airline provides transportation for passengers the way it would produce any product. The units of the commodity produced are homogeneous and identical in nature. Production and inventories are computed in terms of completed products. The processing sequence is specific and predetermined. The production may result in joint products or by-products.
Process Costing: Definition
All such information is provided solely for convenience purposes only and all users thereof should be guided accordingly. Yes, many services are produced in a manner similar to manufacturing goods.
- The total process cost is divided by the total number of items, resulting in an average cost for each item.
- Can you imagine having to determine the cost of making just ONE lego when we can make 1.7 million legos per hour?
- A system of assigning costs used by companies that produce unique products or jobs.
- Production is continuous and the final product or end product is the result of a sequence of processes or operations.
The average costs of homogeneous products can easily be computed. The cost of different processes as well as finished product can be computed conveniently at short intervals, say, daily or weekly. When there is sale of half manufacturing product during the production process. By-product sales added to the main product sales – In this case all costs incurred on main and by-products are deducted from the combined sales of the main product and by-products. FIFO is used when the value of opening WIP is a lump sum figure and the degree of completion is not given. Average method is used when opening WIP is given in terms of materials, labour and overhead but the degree of completion is not mentioned. If the stage of completion and the value in terms of materials, labour and overhead of the opening WIP are mentioned, then either FIFO or Average method, may be used.